Nexus Peptides
MOTS-C: 5-10mg*10 vials
MOTS-C: 5-10mg*10 vials
Couldn't load pickup availability
Share

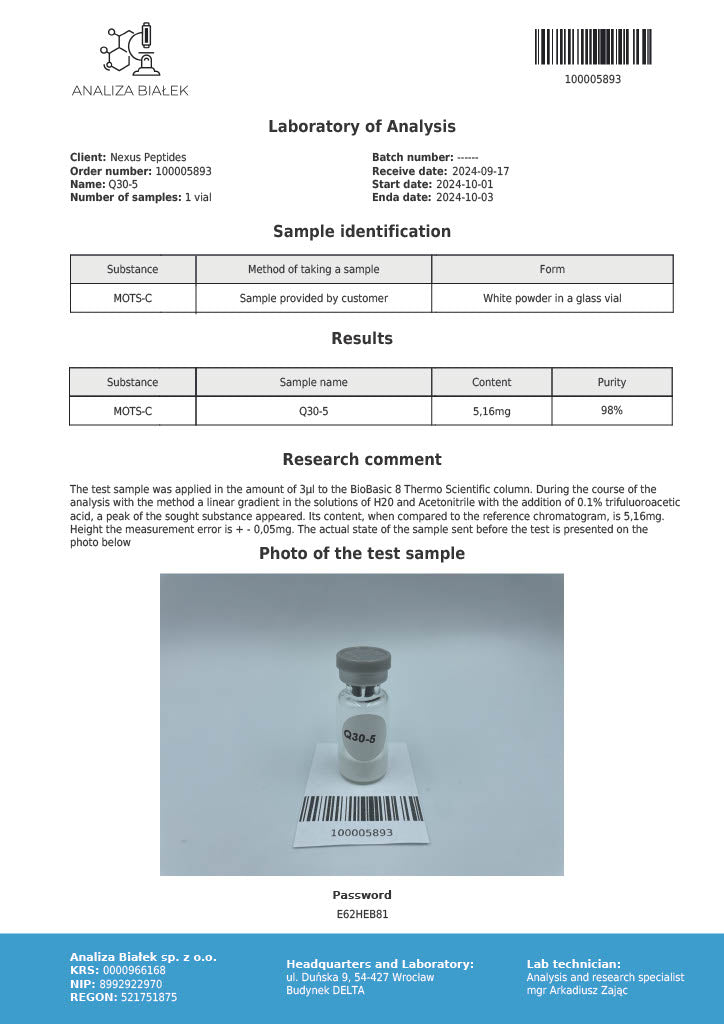
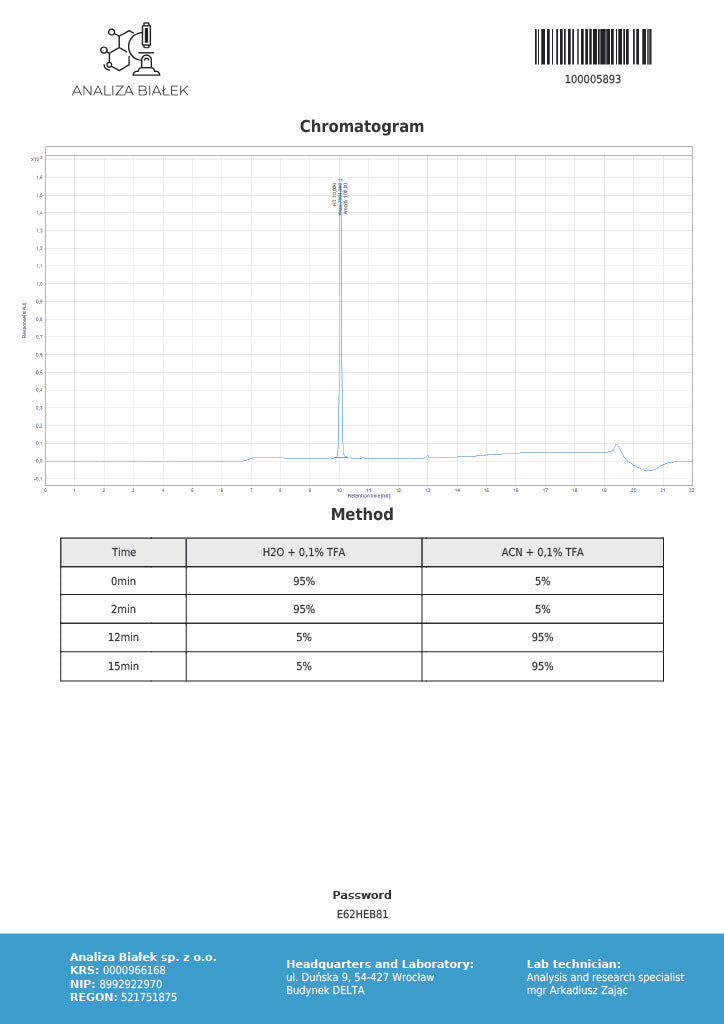

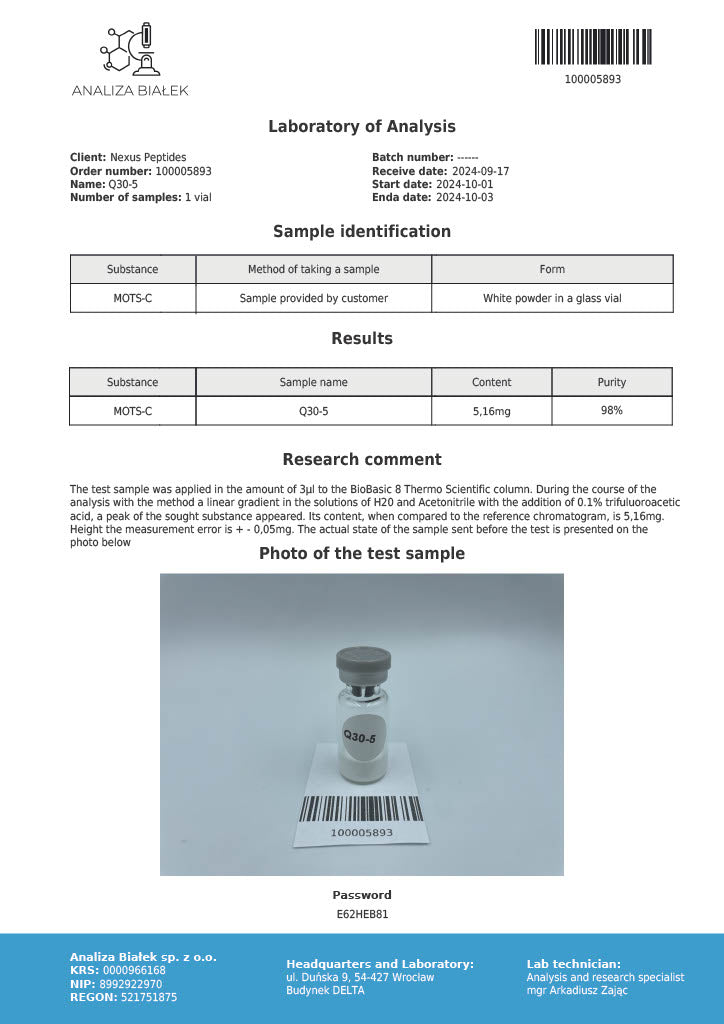
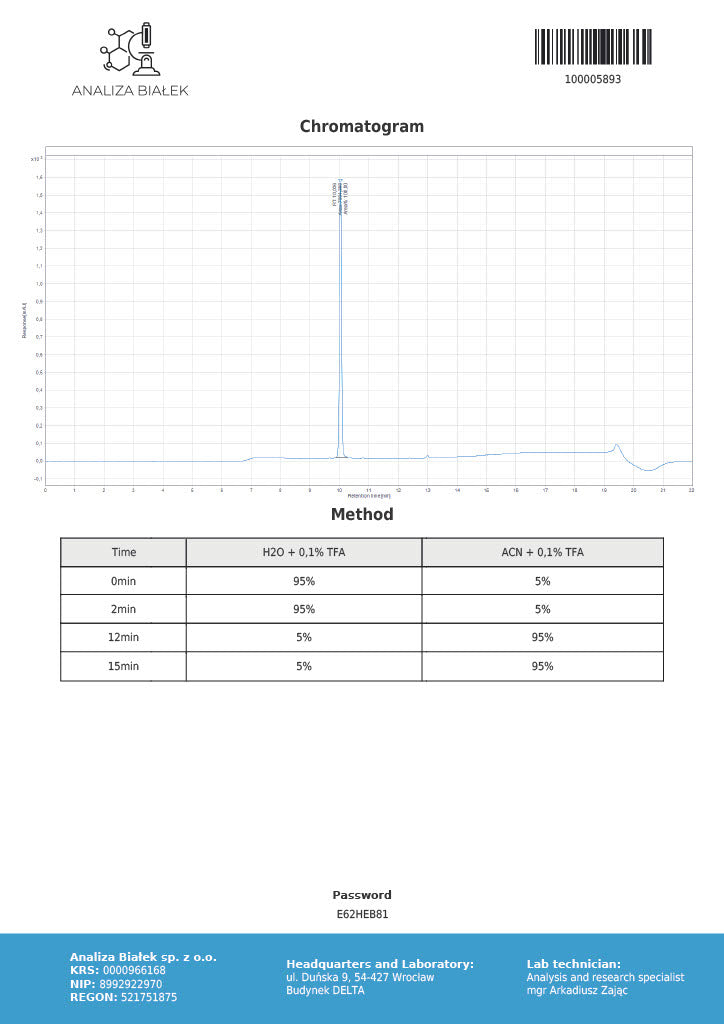
Product Description: MOTS-C
Introduction
MOTS-C is a mitochondrial-derived peptide that has gained attention in scientific research due to its potential role in regulating metabolic processes. This peptide, composed of a short amino acid sequence, is found within the mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles in cells. Researchers investigate MOTS-C for its possible impact on metabolic regulation, mitochondrial function, and its potential role in age-related diseases. As a highly purified peptide, MOTS-C is widely used in laboratory experiments focused on understanding cellular energy homeostasis, mitochondrial dynamics, and other related fields.
What is MOTS-C?
MOTS-C is a peptide encoded by a segment of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Unlike many other peptides, it is unique in that it originates from the mitochondrial genome, which is separate from the nuclear DNA. The peptide is 16 amino acids long and is involved in the regulation of various metabolic pathways. MOTS-C has been identified as part of a broader group of mitochondrial peptides that are thought to regulate cellular functions related to metabolism, energy production, and the cellular stress response.
MOTS-C is considered to be a messenger peptide that communicates between the mitochondria and other parts of the cell. As such, it plays a role in mitochondrial communication, influencing how cells manage energy and respond to different types of metabolic stress. Its potential role in regulating glucose metabolism and its impact on mitochondrial health make it a subject of interest in scientific research.
Potential Different Names
- MOTS-C peptide
- Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-c (MOTS-C)
- Mitochondrial peptide MOTS-C
- Mitochondrial 16-amino acid peptide
- Mitochondrial signaling peptide
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula for MOTS-C is based on its amino acid sequence. For the standard 16 amino acid peptide, the formula is approximately C66H128N24O28S2, although the exact structure may vary depending on any modifications made during peptide synthesis.
Structure
MOTS-C consists of a sequence of 16 amino acids. The specific amino acid sequence of MOTS-C is as follows:
Sequence:
Acetyl-Ser-Ala-Glu-Glu-Gly-Val-Tyr-Gly-Ala-Gly-Ala-Asp-Ser-Gly-Gly-Gly-NH2
This sequence represents the naturally occurring mitochondrial peptide, and its structure is primarily linear. The peptide sequence contains a combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic residues that allow it to interact with both the mitochondrial and cellular components involved in metabolism. Its small size and specific amino acid sequence contribute to its potential activity in various metabolic and mitochondrial pathways.
How Does It Work?
MOTS-C is believed to function as a regulatory molecule within the mitochondria and has been linked to a variety of cellular processes related to metabolism and energy regulation. The mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing energy through oxidative phosphorylation. MOTS-C acts as a messenger that helps communicate between the mitochondria and the rest of the cell, potentially influencing various metabolic pathways, including glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism.
MOTS-C has been studied for its potential effects on cellular responses to metabolic stress and its ability to improve energy homeostasis within the cell. It may also influence the balance between oxidative stress and cellular repair processes, though further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which MOTS-C exerts its effects.
Given its origin from the mitochondrial genome, MOTS-C may also play a role in regulating mitochondrial biogenesis, the process by which new mitochondria are formed within cells. As a signaling peptide, MOTS-C could help the mitochondria adapt to changing energy demands, supporting cellular energy production during times of stress or high metabolic activity.
Conclusion
MOTS-C is a mitochondrial-derived peptide composed of 16 amino acids, with potential roles in regulating metabolic and mitochondrial functions. Researchers are interested in its properties as a signaling peptide that helps manage energy homeostasis within cells and could have an impact on various cellular processes such as glucose metabolism and mitochondrial health. Although further studies are needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms and applications, MOTS-C provides an interesting avenue of research in the field of mitochondrial biology and metabolism.
Disclaimer
MOTS-C is intended for research purposes only. It is not for human consumption, clinical use, or diagnostic purposes. The product should only be handled by professionals in accordance with appropriate laboratory safety guidelines. Researchers are responsible for ensuring proper handling, storage, and disposal of the product in line with institutional and regulatory requirements. This description is provided for informational purposes only, and no health claims are made regarding the use of this product.